BIOLOGY
by Miller & Levine
[complete Table of Contents]

|
Use the pull-down menu to jump to any of the Book's 40 Chapters: |
Additional Resources:
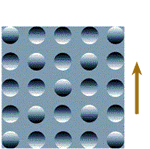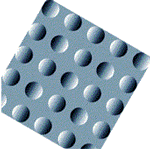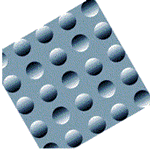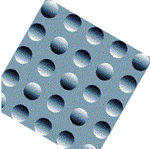
Is your brain telling you the truth?
Are these circles bumps? Or are they depressions?
(You can find the answer in the Hughes
Foundation Booklet on the Senses)
New Information:
In early editions of the Dragonfly book, Figures 35-6 and 35-7 and the description of The Nerve Impulse on pages 898-899 were a bit confusing. I rewrote this section for clarity in June 2002. Click Here for the revision and copies of the both new Figures.
In this chapter, students will read about the organ systems of the human body, focusing primarily on the nervous system. They will read about how nerve cells transmit information, the major divisions of the nervous system, and the effects of various types of drugs on the nervous system.
| Hot Links | Chapter Self-Test |
| Take it to the Net | Teaching Links |
What are Web Codes? |
Web
Codes for Chapter 35: |
![]()
Section 35-1: Human
Body Systems
![]() The eleven organ
systems of the human body work together to maintain homeostasis.
The eleven organ
systems of the human body work together to maintain homeostasis.
Section 35-2: The
Nervous System
![]() The nervous system
controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to
internal and external stimuli.
The nervous system
controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to
internal and external stimuli.
![]() A nerve impulse
begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by its environment.
A nerve impulse
begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by its environment.
Section 35-3: Divisions
of the Nervous System
![]() The central nervous
system relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information.
The central nervous
system relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information.
![]() The sensory division
of the peripheral nervous system transmits impulses from sense organs
to the central nervous system. The motor division transmits impulses from
the central nervous system to the muscles or glands.
The sensory division
of the peripheral nervous system transmits impulses from sense organs
to the central nervous system. The motor division transmits impulses from
the central nervous system to the muscles or glands.
Section 35-4: The
Senses
![]() There are five
general categories of sensory receptors: pain receptors, thermoreceptors,
mechanoreceptors, chemoreceptors, and photoreceptors.
There are five
general categories of sensory receptors: pain receptors, thermoreceptors,
mechanoreceptors, chemoreceptors, and photoreceptors.
Section 35-5: Drugs
and the Nervous System
![]() Stimulants increase
heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate. In addition, stimulants
increase the release of neurotransmitters at some synapses in the brain.
Stimulants increase
heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate. In addition, stimulants
increase the release of neurotransmitters at some synapses in the brain.
![]() Depressants slow
down heart rate and breathing rate, lower blood pressure, relax muscles,
and relieve tension.
Depressants slow
down heart rate and breathing rate, lower blood pressure, relax muscles,
and relieve tension.
![]() Cocaine causes
the sudden release of a neurotransmitter in the brain called dopamine.
Cocaine causes
the sudden release of a neurotransmitter in the brain called dopamine.
![]() Opiates mimic
natural chemicals in the brain known as endorphins, which normally help
to overcome sensations of pain.
Opiates mimic
natural chemicals in the brain known as endorphins, which normally help
to overcome sensations of pain.
![]() Alcohol is a depressant,
and even small amounts of alcohol slow down the rate at which the nervous
system functions.
Alcohol is a depressant,
and even small amounts of alcohol slow down the rate at which the nervous
system functions.
| The Hughes Medical Institute publishers a marvelous booklet on the senses — a perfect complement to Section 35-4. You can use it on-line, or download the whole booklet in PDF format: |