BIOLOGY
by Miller & Levine
[complete Table of Contents]

|
Use the pull-down menu to jump to any of the Book's 40 Chapters: |
Click on the picture for a tutorial on the Chemistry of Water (University of Arizona)
Periodic
Table of the Elements
![]() Chapter 2
Chapter 2 ![]()
The
Chemistry of Life
NEW: Updated Information on Mad Cow Disease, including two brand-new "Virtual Textbook" pages for teaching about mad cow disease (BSE) and its human equivalent (CJD).
| Hot Links | Take it to the Net |
| Chapter Self-Test | Teaching Links |
What are Web Codes? |
Web
Codes for Chapter 2: Science News: Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry SciLinks: Properties of Water SciLinks: Enzymes Self-Test |
![]()
Section 2-1: The Nature
of Matter
![]() The subatomic
particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
The subatomic
particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Because they have the same number of protons, all isotopes of an element
have the same chemical properties.
![]() The main types
of chemical bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds.
The main types
of chemical bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds.
Section 2-2: Properties of Water
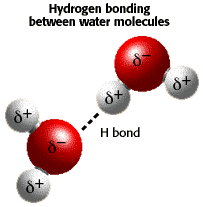
 A water molecule is polar, because there
is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen
atoms.
A water molecule is polar, because there
is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen
atoms.
 Acidic solutions contain higher concentrations
of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values below 7.
Acidic solutions contain higher concentrations
of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values below 7.
 Basic, or alkaline, solutions contain
lower concentrations of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values above
7.
Basic, or alkaline, solutions contain
lower concentrations of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values above
7.
Section 2-3: Carbon Compounds
 Four groups of carbon compounds found
in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and protein.
Four groups of carbon compounds found
in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and protein.
 Living things use carbohydrates as their
main source of energy. Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates
for structural purposes.
Living things use carbohydrates as their
main source of energy. Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates
for structural purposes.
 Lipids can be used to store energy. Some
lipids are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings.
Lipids can be used to store energy. Some
lipids are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings.
 Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary,
or genetic, information.
Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary,
or genetic, information.
 Some proteins control the rate of reactions
and regulate cell processes. Some proteins build tissues such as bone
and muscle. Others transport materials or help to fight disease.
Some proteins control the rate of reactions
and regulate cell processes. Some proteins build tissues such as bone
and muscle. Others transport materials or help to fight disease.
Section 2-4: Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Chemical reactions always involve the
breaking of bonds in reactants and the formation of new bonds in products.
Chemical reactions always involve the
breaking of bonds in reactants and the formation of new bonds in products.
 Chemical reactions that release energy
often occur spontaneously. Chemical reactions that absorb energy will
not occur without a source of energy.
Chemical reactions that release energy
often occur spontaneously. Chemical reactions that absorb energy will
not occur without a source of energy.
 Cells use enzymes to speed up chemical
reactions that take place in cells.
Cells use enzymes to speed up chemical
reactions that take place in cells.
Click Here for Science News articles
on the Properties of Matter and Biological Chemistry